Plastic Production Line: Streamlining High-Volume Manufacturing with Integrated Automation
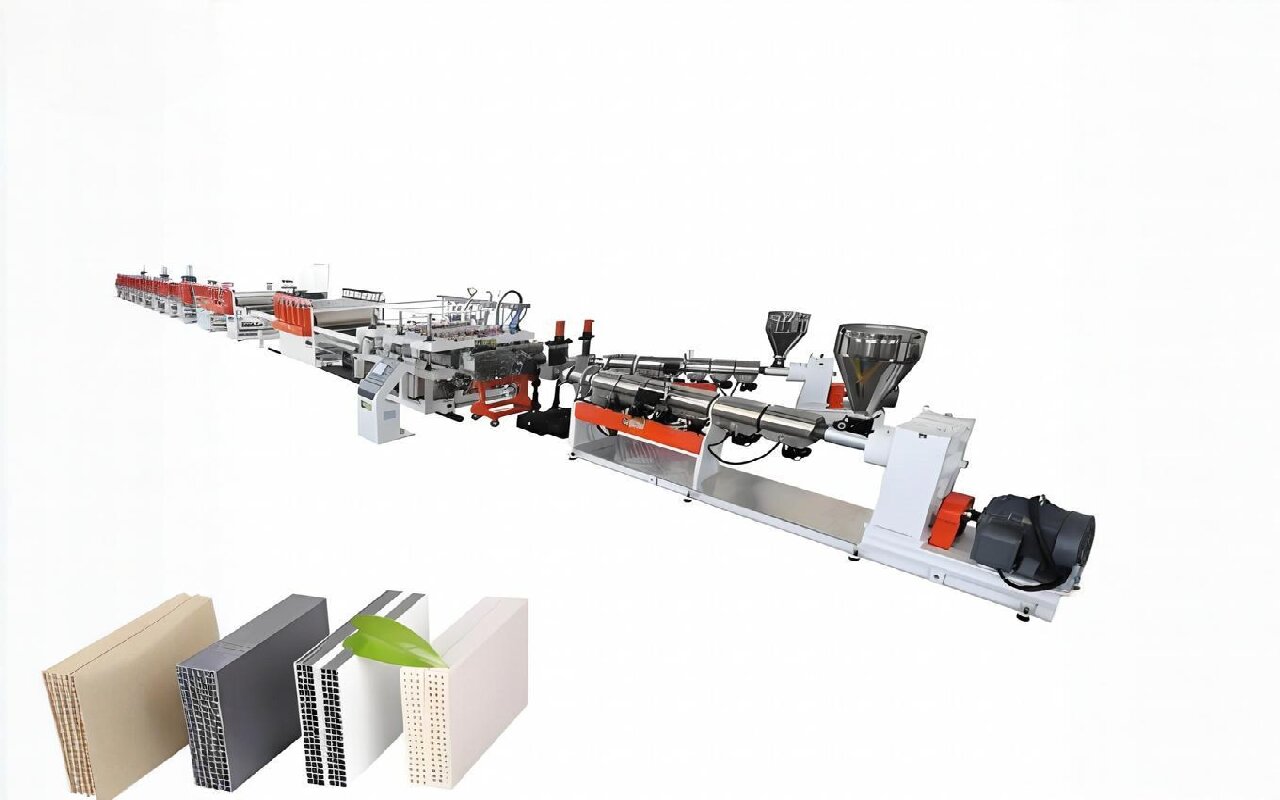
A plastic production line is a comprehensive system that transforms raw polymers into finished products through sequential processes like extrusion, molding, and finishing. These lines are engineered for efficiency, scalability, and precision in industries ranging from packaging to automotive.
What is a Plastic Production Line?
It integrates multiple machines, including extruders, molds, cooling systems, and quality control devices, to automate plastic product manufacturing.
Types of Production Lines
- Extrusion Lines:
- Produces continuous profiles (pipes, sheets) using single/twin-screw extruders.
- Injection Molding Lines:
- Manufactures complex parts (e.g., bottle caps, automotive dashboards) with high-pressure molds.
- Blow Molding Lines:
- Creates hollow products (bottles, containers) by inflating molten plastic parisons.
- Compression Molding Lines:
- Used for thermoset plastics (e.g., Bakelite) in electrical components.
Core Benefits
- High Throughput: Produces thousands of units per hour with minimal downtime.
- Consistency: Automated controls ensure uniform product dimensions and quality.
- Flexibility: Quick changeovers between product designs via modular tooling.
- Resource Optimization: Closed-loop systems recycle water and excess heat.
Industry Applications
- Packaging: Food containers, shrink films, and pharmaceutical blister packs.
- Construction: PVC windows, insulation boards, and plumbing fittings.
- Consumer Goods: Toys, household appliances, and electronic casings.
Operational Workflow
- Material Preparation: Dry and mix resins with additives (colorants, stabilizers).
- Processing: Melt polymers in extruders or molding machines.
- Shaping: Form molten plastic into products via molds or dies.
- Cooling: Use water baths or air jets to solidify products.
- Finishing: Trim excess material, apply coatings, or print labels.
Key Automation Technologies
- Robotic Arms: Handle part removal and assembly.
- Machine Vision Systems: Detect defects like warping or air bubbles.
- IoT Integration: Monitor energy consumption and predict maintenance needs.






