Plastic Pipe Machinery: Essential for Durable and Efficient Pipe Production
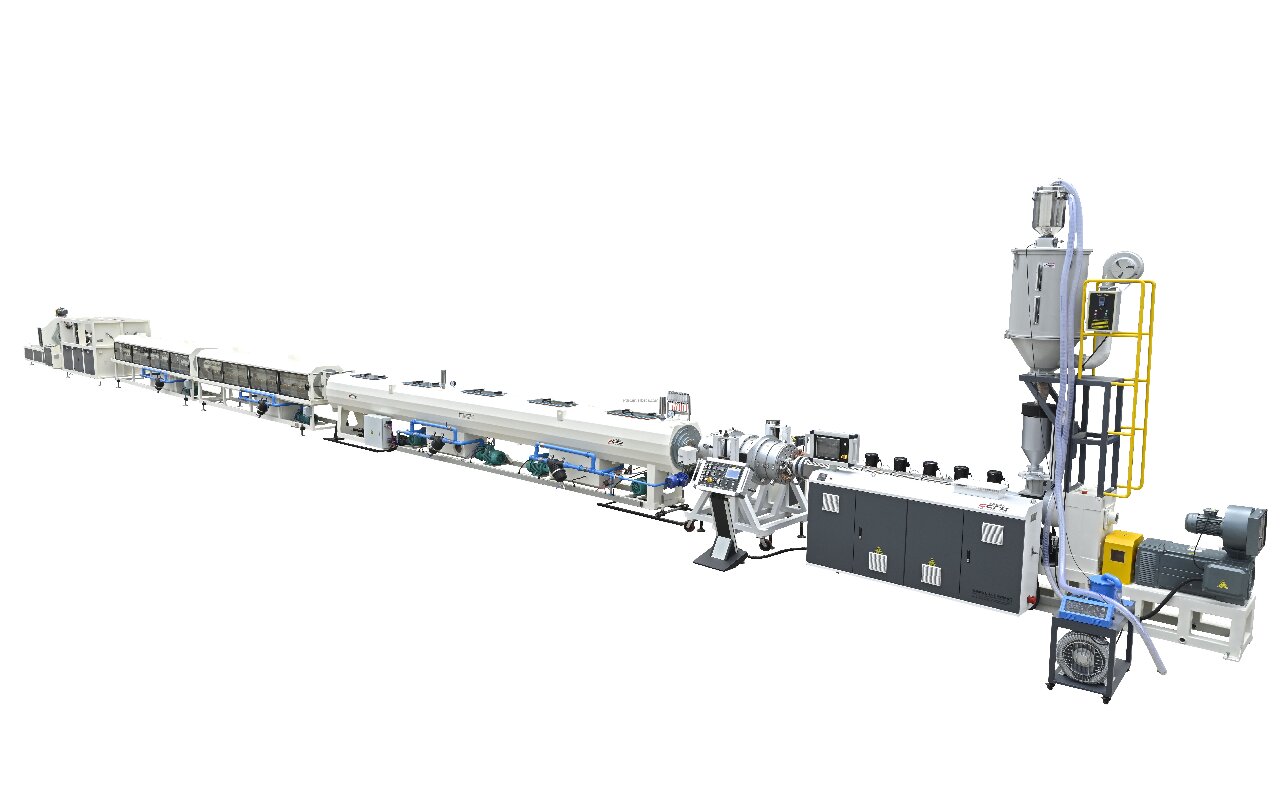
Plastic pipe machinery refers to equipment used to manufacture plastic pipes for water supply, drainage, gas distribution, and industrial applications. These machines ensure high-quality, long-lasting pipes through extrusion and molding processes. This article explains plastic pipe machinery, its types, functions, benefits, and applications.
What is Plastic Pipe Machinery?
Plastic pipe machinery includes extruders, molds, and cooling systems that melt plastic, shape it into pipes, and solidify the final product. It is critical for infrastructure and construction projects.
Types of Plastic Pipe Machinery
- Single-Screw Extruders:
- Basic machines for producing standard PVC or HDPE pipes.
- Twin-Screw Extruders:
- Handle complex materials and high-output production.
- Corrugated Pipe Machines:
- Create ribbed pipes for drainage and cable protection.
- Multi-Layer Pipe Machines:
- Produce pipes with layers of different materials for enhanced properties.
Functions and Benefits
- Durability:
- Produces pipes resistant to corrosion and chemicals.
- High Output:
- Enables continuous pipe production for large projects.
- Customization:
- Adjust diameter, thickness, and material composition.
- Cost Savings:
- Reduces material waste and labor costs.
- Sustainability:
- Supports recycling of plastic materials.
Applications
- Water Supply:
- Manufacture pipes for drinking water and irrigation.
- Drainage Systems:
- Produce corrugated pipes for sewage and stormwater.
- Gas Distribution:
- Create high-pressure pipes for gas transportation.
- Industrial Use:
- Make chemical-resistant pipes for factories.
- Construction:
- Supply pipes for HVAC and electrical conduits.
Key Advantages Over Traditional Methods
- Consistency:
- Ensures uniform pipe dimensions and quality.
- Speed:
- Faster than manual pipe manufacturing.
- Automation:
- Minimizes human intervention and errors.
Operation Steps
- Material Feeding:
- Load plastic pellets into the extruder.
- Extrusion:
- Melt and shape plastic into a pipe through a die.
- Cooling:
- Use water baths or air cooling to solidify the pipe.
- Cutting and Coiling:
- Cut pipes to length or coil them for storage.
Maintenance Tips
- Clean extruder screws and dies regularly.
- Inspect cooling systems for blockages.
- Lubricate conveyor belts and cutting tools.
Conclusion
Plastic pipe machinery is vital for modern infrastructure, providing durable and efficient piping solutions. From water supply to industrial applications, these machines support sustainable and cost-effective construction.






