Biomass Briquette Machines: Turning Waste into Clean Energy with Cold-Pressing Technology
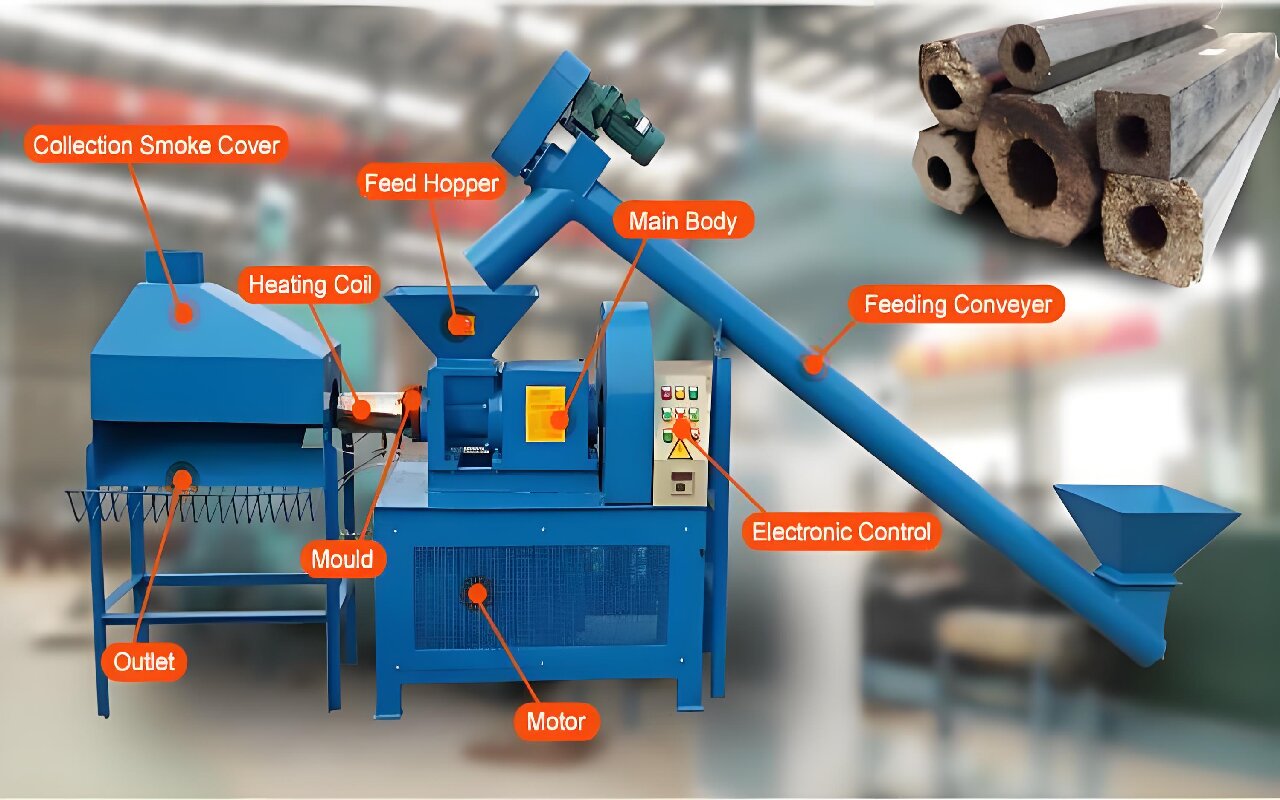
Biomass briquette machines are devices that compress agricultural or forestry waste (e.g., sawdust, rice husks, straw) into dense, solid fuel blocks at room temperature. These machines eliminate the need for high heat or chemicals, making them an eco-friendly solution for renewable energy production. This article explains what biomass briquette machines are, their types, functions, advantages, and related applications.
What is a Biomass Briquette Machine?
A biomass briquette machine is a mechanical press that uses high pressure to bind loose organic materials into compact briquettes or pellets. These briquettes serve as a sustainable alternative to coal or firewood, reducing waste and greenhouse gas emissions.
Types of Biomass Briquette Machines
- Screw Extruder Machines:
- Use a rotating screw to compress materials into cylindrical briquettes. Suitable for fine, dry materials like sawdust.
- Piston Press Machines:
- Employ a hydraulic or mechanical piston to create high-pressure briquettes. Ideal for fibrous materials (e.g., straw, coconut shells).
- Hydraulic Press Machines:
- Generate extreme pressure to form dense briquettes, often used for industrial-scale production.
- Manual Briquette Presses:
- Hand-operated devices for small-scale or household use.
Functions and Benefits
- Waste Recycling:
- Convert agricultural residues, forestry waste, or municipal biomass into usable fuel.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Briquettes burn longer and hotter than raw biomass, improving energy output.
- Cost Savings:
- Reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower energy costs for households and industries.
- Eco-Friendly:
- Reduce deforestation and carbon emissions by replacing coal and firewood.
- Easy Storage & Transport:
- Compact briquettes take up less space and are easier to handle than loose biomass.
Applications
- Household Heating:
- Replace firewood in stoves or boilers for cooking and heating.
- Industrial Boilers:
- Fuel factories, brick kilns, or power plants with biomass briquettes.
- Agricultural Use:
- Process farm waste into fuel for on-site energy needs.
- Disaster Relief:
- Provide a quick energy source in areas with limited fuel access.
Key Considerations for Operation
- Material Preparation:
- Biomass must be dried (moisture <15%) and shredded for optimal compression.
- No Binders Required:
- Lignin in biomass acts as a natural binder under high pressure.
- Maintenance:
- Regularly clean the machine and lubricate moving parts to prevent wear.
Comparison to Traditional Fuel
Unlike coal, biomass briquettes produce minimal ash and smoke. They are carbon-neutral, as the CO₂ released during burning is offset by plant growth.
Conclusion
Biomass briquette machines are a cornerstone of sustainable energy systems, transforming waste into valuable fuel. Their simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and environmental benefits make them essential for rural and urban communities alike. By adopting this technology, industries and households can reduce waste, cut energy costs, and contribute to a greener planet.






